Blog más reciente
La diferencia entre el láser ultravioleta de 355 nm y el láser infrarrojo de 1064 nm
Dec 16 , 2022The difference between 355nm ultraviolet laser and 1064 nm infrared laser
Infrared lasers and ultraviolet lasers are the two most widely used lasers, so what is the difference in the processing of these two lasers? How to choose laser marking with higher requirements?
Infrared YAG laser with a wavelength of 1.06 μm is the most widely used laser source in material processing. However, many plastics and some special polymers (such as polyimide) that are widely used as substrate materials for flexible circuit boards cannot be finely processed by infrared treatment or "thermal" treatment.
Because "heat" deforms the plastic, damage in the form of carbonization occurs on the edge of the cut or drilled hole, which may lead to structural weakening and parasitic conductive pathways, and some post-processing steps have to be added to improve the processing quality. Therefore, infrared lasers are not suitable for processing some flexible circuits. In addition, even at high energy densities, the wavelength of infrared lasers cannot be absorbed by copper, which further severely limits its application range.
The output wavelength of ultraviolet lasers is below 0.4 μm, which is the main advantage of processing polymer materials. Unlike IR processing, UV microprocessing is not thermal in nature, and most materials absorb UV light more readily than IR light. High-energy ultraviolet photons directly destroy molecular bonds on the surface of many non-metallic materials, and parts processed by this "cold" photoetching process have smooth edges and minimal carbonization.
Moreover, the characteristics of the short wavelength of ultraviolet light are superior to the mechanical micro-processing of metals and polymers. It can be focused to sub-micron points, so it can process fine parts, even at low pulse energy levels, it can also get high energy density, and effectively process materials. Micro-holes are in the industry. The application in has been quite extensive, and there are two main ways of formation:
One is to use an infrared laser: to remove the material by heating and vaporizing (evaporating) the substance on the surface of the material, this method is usually called thermal processing. Mainly adopt YAG laser (wavelength is 1.06μm).
El segundo es usar láser ultravioleta: los fotones ultravioleta de alta energía destruyen directamente los enlaces moleculares en la superficie de muchos materiales no metálicos, de modo que las moléculas se separan del objeto. Este método no genera mucho calor, por lo que se denomina procesamiento en frío y utiliza principalmente láser ultravioleta (la longitud de onda es de 355 nm).
La comparación entre el láser ultravioleta y el láser infrarrojo ordinario es la siguiente:
Láseres ultravioleta y láseres infrarrojos (la diferencia entre los láseres ultravioleta y los láseres infrarrojos)
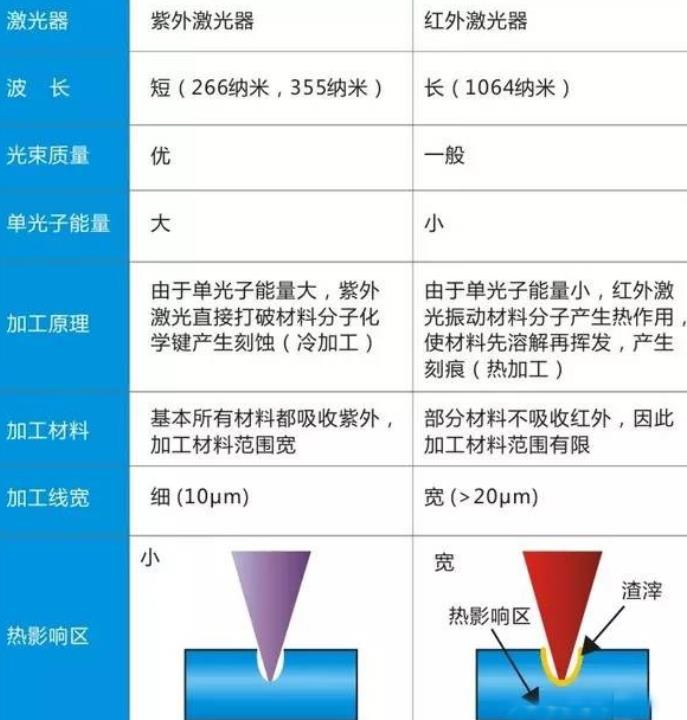
A través de la tabla anterior, no es difícil encontrar que el láser ultravioleta tiene una ventaja absoluta en el marcado ultrafino y el marcado de materiales especiales debido a su punto de enfoque extremadamente pequeño y su mínima zona afectada por el calor de procesamiento.