
Láseres ultravioleta (UV) Marcas Alambre Cable Materiales de aislamiento
Sep 16 , 2022According to IOP Handbook of Laser Technology, in 1999 approximately 22,000 laser marking machines were in use in various industries worldwide. Hexa Research expects overall laser market to reach $3bln USD in 2024. It seems quite possible that in a few years everything that needs to be marked will be marked with lasers including fruits and vegetables and most definitely wires and cables.
This article describes the basic principles of UV laser marking of wires and cables for aerospace industry and its applicability to other markets.
Direct printing on wires and cables with Ultra-violet (UV) lasers has been extensively tested and accepted within the aerospace industry both by OEMs and by the end users. It is covered by several documents and standards issued by SAE International and reflected in the production specification of large and small frame aircrafts for commercial, industrial, and military use. The OEM list includes Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, Sikorsky, Gulfstream, Bombardier, Pilatus, and many others. It is also used by governmental agencies such as DOD, NASA, FAA, etc. End users employ UV laser marking machines during scheduled maintenance and repair procedures.
UV lasers leave a permanent indelible high-resolution mark on the substrate surface. To understand the phenomenon, we must consider how a laser beam interacts with material. For example, the beam can be completely reflected from a surface, as a sun ray from a mirror, or propagate unaffected, as a sun ray through clear glass window. In these cases, no trace will be left on a surface. To mark a material, at least part of the laser radiation must be absorbed directly on or near the material’s surface.
Depending on laser and material properties there are a few possible scenarios (Fig.1):
The irradiated material evaporates, leaving relatively sharp border trenches on the surface.
The irradiated material melts and spills from the inside out, creating hills and valleys in the middle of a plain.
The irradiated material heats up and produces gaseous components that react with atmospheric oxygen, depositing a product of combustion (such as soot) on the surface.
Color change. The material changes color without any other visible surface modifications.
All of the above.
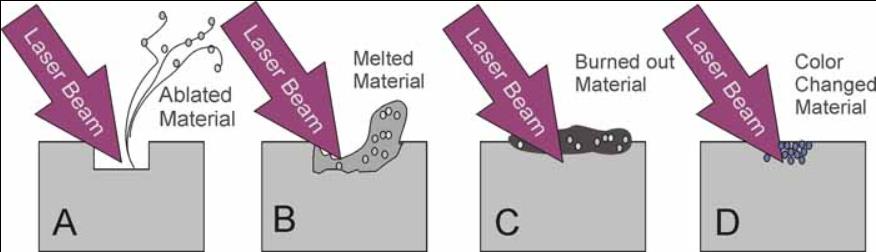
Fig.1. Laser-Surface Interactions.
Ablation is the cleanest way to alter the surface but provides low marking contrast because the affected area does not change color. Making deeper and wider marks improves legibility but reduces material integrity that is clearly unacceptable for aerospace applications. One possibility is applying additional layer of wire insolation and then selectively removing it exposing the undercoat of a different color, but this does not look very practical either.
Melting and burning marking processes are subject to long-term durability problems because the melted material and burned-out deposit may not stick well to the unaffected area. That resembles a 21st century hot stamping technique. Of course, this version is more advanced, flexible, and precise but it is still hot stamping with all its well-known deficiencies.
Color change can be an excellent solution under the conditions that it does not alter the material properties, provides sufficient contrast, good durability, and long-term stability. UV laser marking of aerospace wires and cables satisfies all these requirements.
Fig.2 shows ETFE, and PTFE insulated wires processed with Tri-Star Technologies M-100L-FG wire marking system. Well defined, legible prints stay intact even after extensive accelerated thermal aging.
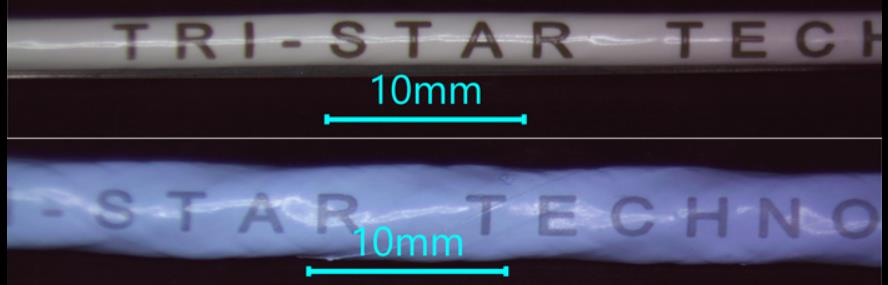
Fig.2. UV laser marking on ETFE (top) and PTFE (bottom) wires.
Marking cross sections (Fig.3) confirm that darkening zone extends 10-20um under the surface ensuring that marking cannot be altered or removed without physically destroying the top layer of the insulation.
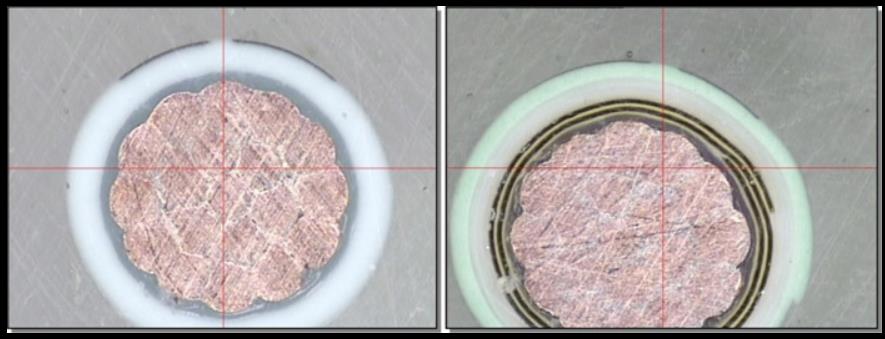
Fig.3. Marked wire cross sections for BMS13-48T10C01G022 (left) and BMS13-60T44C01G022 (right).
The question is how a light-colored polymer surface turns dark under laser exposure without burning or melting. The answer is magic substance called Titanium Dioxide (TiO2). Luckily enough, this is a commonly used pigment that wire manufacturers use to make insulation look white or otherwise light-colored, such as gray, blue, green, yellow, pink, etc.
An optical band gap around 3.1 electron volts accounts for TiO2’s intense absorption of UV radiation with wavelengths shorter than 380 nanometers. Irradiation with a UV laser permanently turns TiO2 particles from white to blue/black. The same effect occurs when those particles are embedded into a substrate. Ideally, laser radiation does not react with the base material and passes freely through the substrate surface. In contrast, the pigment particles within the substrate interact with the laser beam that modifies the particles’ structure and appearance, including color. For example, thin PTFE films are practically transparent to the UV light while small (~0.3u) TiO2particles randomly distributed through the insulation layer strongly absorb the light and change color.
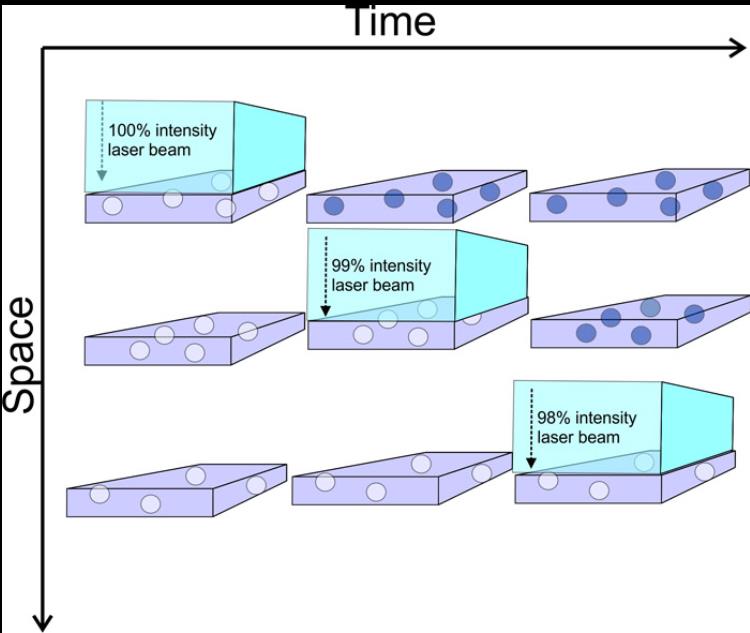
Fig.4 illustrates the process in space and time. An incident laser beam penetrates freely through the first material layer losing a small fraction (e.g., 1%) of its total energy on interaction with originally white TiO2 particles, turning them black. The same happens on the second layer and so on until most of the laser pulse energy is absorbed within the top 50-100 layers. In reality, the process is quite limited both in time and space as total pulse duration is normally below 30ns and marking depth does not exceed 50um or so.
Fig.4. Schematic representation of UV laser beam path through a transparent media dopped with TiO2 particles.
Short nanosecond laser pulses prevent regular heat exchange between the additives and the surrounding material, limiting any structural and/or chemical modifications to the pigment particles themselves. Clearly this mark cannot be easily removed as most of it is distributed through the top layer but not on the very surface.
The question of what exactly happens to TiO2 particles under intensive UV light exposure is outside of the scope of this article, but the resulting change of color is irreversible. For example, long-term stability of UV laser marking on TiO2 doped ETFE films was investigated in McDonnell Douglas Research Laboratories in 1990. The marking showed little change during either thermal aging (770 hours at 229oC) or simulated solar irradiation (equivalent to 17 years of UV exposure in the Arizona desert).
El contraste de marcado es proporcional a la concentración de TiO2; sin embargo, cantidades excesivas pueden dañar el aislamiento. Normalmente, un 2-4% en peso es suficiente para lograr un buen contraste. La Tabla 1 especifica los niveles de contraste típicos que se pueden lograr mediante la impresión láser UV directa en las construcciones de alambre comúnmente utilizadas en la industria aeroespacial.
Tabla 1. Alambres y cables marcables con láser UV
Especificación del cable Color Aislamiento Marcado Contraste
BMS 13-48 Blanco Extruido XLETFE Excelente
BMS 13-58 Envoltura de cinta de PTFE gris Bueno
BMS 13-60 Envoltura de cinta de PTFE blanca Buena
BMS 13-60 Envoltura de cinta de PTFE verde Marginal
M22759/05,06,08 PTFE extruido blanco Pobre
M22759/07 Marginal de PTFE extruido blanco
M22759/09,10,11,12, 20,21,22,23,28,29,30,31 TFE extruido blanco marginal
M22759/16,17,18,19 ETFE extruido blanco Bueno
M22759/32,33,35,41,42,44,45,46 Blanco Extruido XLETFE Muy Bueno
M22759/34,43 Blanco Extruido XLETFE Excelente
M22759/80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92 Envoltura de cinta de PTFE blanca Buena
M85485/5,6,9,10 Violeta Extruido XLETFE Muy bueno
M25038 Envoltura de cinta de PTFE blanca Pobre
M27500 SP2S23 Blanco Extruido XLETFE Muy bueno
M27500/20 L3T08 PVDF Extruido Blanco Excelente
M27500/20 P2G23 PVC blanco / NYLON Muy bueno
M27500/22 C1G23 Blanco PVC/VIDRIO/NYLON Muy bueno
M27500/22 SP5S23 Blanco Extruido XLETFE Muy Bueno
M27500/24 C3G23 Blanco PVC/VIDRIO/NYLON Muy bueno
M81044 PVDF Extruido Blanco Excelente
También se pueden marcar otros tipos de cables siempre que contengan el pigmento mágico. El requisito de tener TiO2 en la capa exterior de una cubierta es la principal limitación de la tecnología de marcado descrita anteriormente. En la mayoría de las aplicaciones, el TiO2 se utiliza como agente de pigmentación blanco y se vuelve negro con la irradiación del láser UV. Por lo tanto, solo los cables de colores claros se pueden imprimir de forma legible.
El resto de los cables también se pueden marcar con láser a través de los diferentes mecanismos que se muestran en la Fig. 1. Sin embargo, lo más probable es que estas marcas no cumplan con los estrictos estándares aeroespaciales a menos que encontremos otro pigmento mágico que, por ejemplo, se vuelva blanco. de negro tras la exposición al láser verde.